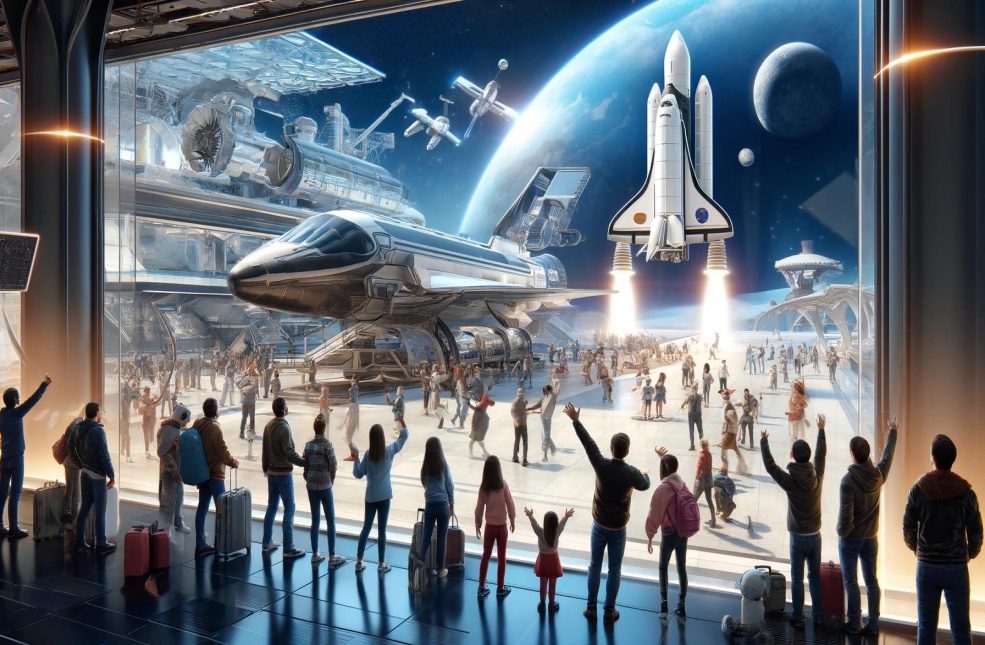
Space enthusiasm can be baffling to the uninitiated. Why are some nerds so enamored with space? Why should society spend any resources to go there? Why are billionaires jockeying to realize their visions for space development? Why do we give NASA over $20 billion and the Space Force as much? Why should we do any of this if we still have problems on Earth?
Imagine a switch that turned off America’s space capabilities.
If you flip it, there’s no more NASA. Space Force and SpaceX disappear. NOAA collects all the weather and climate data from space. It goes offline. The National Reconnaissance Office is blind.
What would happen? The quality of life on Earth would degrade. Authoritarian powers would threaten democracies. We would lose vital scientific resources. Our institutions would experience a slow decline.
We must continue investing in space to flourish as a society and a species.
Improving Daily Life on Earth
Space impacts modern life through satellites. They are crucial for broadcasting and safety on planes and ships. They connect remote areas, such as oil platforms, to civilization. SpaceX’s Starlink is expanding. Soon, millions of rural homes will have high-speed internet.
Satellites also enhance positioning and navigation. GPS keeps running planes, ships, and ride-sharing services like Uber and Lyft. With it, many smartphone functions and in-dash navigation systems would be helpful.
Satellites also improve weather forecasting. In the past, a lack of accurate forecasts led to disasters, such as the 1900 Galveston hurricane. Today, NOAA’s GOES system provides reliable forecasts, saving lives and property.
Space technology benefits the Earth in many ways. NASA’s research has led to innovations like vertical farming. It saves resources and delivers fresh produce. Techniques developed for space have improved aeroponics and LED growing systems.
Microgravity revolutionizes manufacturing, improving drug production, carbon nanotubes, and silicon wafers. SpaceX’s Starship makes space manufacturing viable, with startups like Varda offering zero-gravity services.
Scientists manufacture ZBLAN optical fiber in space. It performs better and costs less for undersea cables, improving connectivity.
Protecting and Preserving Democracy
Space investments help democratic countries defend against authoritarian regimes like China and Russia. Space is the ultimate high ground for military advantage.
From space, we can watch battlefields and spy on enemy movements. Satellites provide crucial imagery, as seen in Ukraine, where they track Russian troops. Some satellites use synthetic aperture radar to see through clouds and at night.
Advanced spy satellites. Some, like the USA-245, get close to Earth for high-resolution photos. Other countries’ satellites can stalk these satellites to understand our surveillance capabilities.
America’s early warning system relies on SBIRS, which detects missile launches. The Next Generation Overhead Persistent Infrared System will soon replace SBIRS. The current defense focuses on short- and medium-range missiles. Yet, tracking from space is critical for future improvements. It will help against long-range and hypersonic missiles.
No country has declared space weapons yet. But they have concepts like the US Air Force’s “Rods from God.” These could strike targets with kinetic energy.
Warfare relies more on space, leading significant powers to develop anti-satellite weapons. In conflicts, attackers may destroy many satellites, reducing surveillance, positioning, and missile warnings. Debris from attacks could restrict access to low Earth orbit.
To counter this, we need many satellite constellations, not single targets. We also need more agile satellites. And we need satellites in ultra-low Earth orbit. Debris clears there, and the imagery is sharp.
Enriching Science
Space investment is valuable for scientific knowledge. If you believe in science, you should support space exploration. Our advancements in science owe much to space exploration.
Space provides crucial climate data. NOAA’s GOES satellites have tracked air changes for years. They help us understand and manage urban heat islands and land-use changes.
Space also helps us understand Earth’s past. For example, Earth’s oceans may have formed from asteroid collisions. NASA’s Dawn spacecraft found that 30 percent of the mass of Ceres, a giant asteroid, is water. This suggests that asteroids could have delivered water to Earth.
Space telescopes like Hubble have revolutionized astronomy. They offer clear views of the universe and estimate its age. The James Webb Space Telescope will soon make discoveries. It will prove dark matter theories and find signs of life on exoplanets.
Life on Earth might have come from space. Scientists have found organic molecules in interstellar space and asteroid samples.
Space allows us to study extreme physics, like those in black holes and supernovae. High-energy astrophysics thrives with advanced instruments observing these unique conditions.
Exploring space is critical to science. It helps us understand physics and explore the origins of life and the universe.
Satisfying Humanity’s Need for a Frontier
Continued investment in space is crucial because it provides a new frontier. Human institutions need renewal. Exploring new, harder lands fosters innovation and clarity.
Some argue that we should focus on Earth’s unexplored areas, such as the oceans or Antarctica. Yet, these areas offer challenges that are different from those in space. On Mars, settlers will face life-or-death situations. This will foster a survival mindset and drive innovation.
Space exploration also offers endless opportunities. After Mars, we can explore the asteroid belt, the moons of Jupiter and Saturn, and even terraform Venus. Space limits Earth’s frontiers, but it offers unlimited expansion.
Investing in space is essential for the health and innovation of human institutions. The Milky Way has many resources. Space exploration will change our culture and progress.