C60 has become a focal point in the natural health community, often praised for its diverse benefits.
Some include sunburn prevention, promoting hair growth, and enhancing longevity. Experts also state that C60 can shield the body from damage caused by free radicals.
In this article, we explore the basics of C60 to give you a better understanding of this molecule. If you’re interested in such products like edibles, tinctures, and drops for humans and pets, you can check Enspire Brand, some of which contain C60.
What are Molecules?
A molecule is a neutral assembly of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds. The atom represents the smallest unit of an element, all sharing the same number of protons and indivisible by chemical means.
However, molecules form the basic unit of a pure substance, comprising multiple atoms. Each molecule maintains a consistent composition, with a fixed ratio of its constituent atoms, resulting in identical chemical properties across identical molecules.
Unlike atoms, molecules can be disassembled through chemical reactions, breaking their bonds and yielding individual atoms.
Some Molecule Examples
Molecules vary in composition, comprising either multiple atoms of a single element or a combination of different elements. Some examples include:
- NaCl (table salt)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
- Hemoglobin (C738H1166N812O203_S2Fe)
- O3 (ozone)
- H2O (water)
- Vitamin C or ascorbic acid (C6H8O6)
- C6H12O6 (glucose)
- CaO (calcium oxide)
- N2 (nitrogen)
Types of Molecules
Molecules are categorized based on their structure:
- Diatomic molecules, composed of two atoms, can be either homonuclear (consisting of the same element) or heteronuclear (containing different elements). Examples include O2 and HCl.
- Polyatomic molecules consist of more than two atoms, such as glucose (C6H12O6) and water (H2O).
- Macromolecules, notably large, are composed of subunits, exemplified by proteins and DNA.
Molecules are also classified by their chemical bonds:
- Covalent molecules, comprising atoms joined by covalent bonds, consist mainly of nonmetals. Pure covalent molecules, like H2 and O3, feature atoms with equivalent electronegativity, while polar covalent molecules, such as water (H2O) and hydrochloric acid (HCl), exhibit slight differences in electronegativity.
- Ionic molecules, containing both metals and nonmetals, demonstrate extreme polarity due to significant electronegativity differences between cations and anions. Notable examples include salt (NaCl), ammonium acetate (NH4CH3CO2), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
Fullerenes: A New Kind of Carbon Molecule
Carbon, widely studied and fundamental to life, is one of the most common elements, forming the basis of organic chemistry. Fullerene is a class of hollow carbon molecules that can take the form of closed cages known as “buckyballs” or cylindrical structures called carbon “nanotubes”.
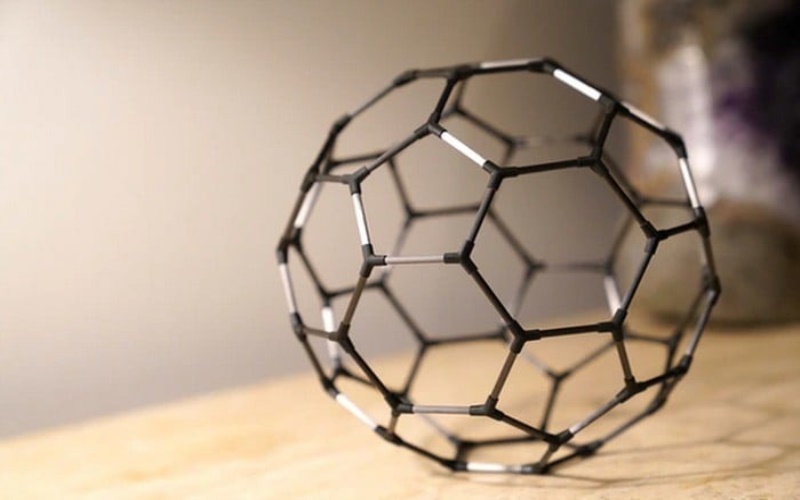
The discovery of the first fullerene occurred in 1985, credited to Sir Harold W. Kroto, Richard E. Smalley, and Robert F. Curl, Jr. They utilized a laser to vaporize graphite rods in a helium atmosphere, resulting in the formation of cage-like molecules composed of 60 carbon atoms (C60).
These molecules form a hollow sphere with 12 pentagonal and 20 hexagonal faces, resembling a football or soccer ball. In recognition of its architecturally inspired structure, the C60 molecule was named buckminsterfullerene, or simply the buckyball, after R. Buckminster Fuller, the American architect known for his geodesic dome.
The Application of Fullerenes
Fullerenes, especially the highly symmetrical C60 sphere, possess a beauty and elegance that captivate both scientists and nonscientists alike. They bridge aesthetic gaps across various disciplines, including the sciences, architecture, mathematics, engineering, and visual arts.
Prior to their discovery, only two well-defined allotropes of carbon were known: diamond (a three-dimensional crystalline array of carbon atoms) and graphite (composed of stacked sheets of two-dimensional hexagonal arrays of carbon atoms). Fullerenes constitute a third form, and it is remarkable that their existence remained elusive until the end of the 20th century.
Their discovery revolutionized the understanding of sheet materials and inaugurated a new chapter in nanoscience and nanotechnology—the “new chemistry” of complex atomic-scale systems exhibiting advanced materials behavior.
In particular, nanotubes exhibit a wide range of novel mechanical and electronic properties. They are exceptional conductors of heat and electricity, with astonishing tensile strength. These properties hold promise for applications in electronics, structural materials, and medicine. However, practical applications will only be feasible once precise structural control is achieved in the synthesis of these materials.
The Use of C60 as a Health Supplement
According to researchers, C60 has potential benefits for various health concerns, including:
- Protection against sun damage and sunburns
- Radiation protection
- Combating viral infections
- Reducing oxidative stress
- Targeting amyloid plaques in the brain associated with Alzheimer’s disease
- Alleviating allergies
- Enhancing brain activity
- Stimulating the immune system against cancer
- Promoting healthy hair growth
These diverse benefits make C60 a promising molecule. The researchers concluded that fullerene could promote longevity in rats, suggesting exciting possibilities for human health. They highlighted C60 as a potentially efficient material for extending lifespan.
C60 fullerene acts as a potent antioxidant, combating harmful free radicals like superoxide in the body. While superoxide is a natural byproduct of cellular metabolism, its accumulation is undesirable.
According to a 2013 study, scientists propose that C60 absorbs protons, creating a positive charge. As it traverses cell membranes and enters mitochondria, the body’s energy-producing organelles, it reduces oxidative stress.
Fat Soluble vs Water Soluble C60
It’s worth noting the distinction between fat-soluble and water-soluble C60. Mice given water-soluble Carboxyl C60 experienced a modest increase in lifespan, from 120 to 128 days, representing a 6.67% increase. In contrast, regular C60 dissolved in olive oil nearly doubled the mice’s lifespan.
However, there have been conflicting findings. A more recent 2021 study did not replicate the same results, showing no improvement in the animals’ lifespan.
Key Takeaways
- Molecules are the basic unit of pure substances, made from 2 or more atoms linked by chemical bonds.
- They come in various forms, from simple water (H2O) to complex DNA.
- Fullerenes are a new class of carbon molecules shaped like cages (buckyballs) or tubes (nanotubes).
- C60 fullerene (made of 60 carbon atoms) has interesting properties and potential health benefits as an antioxidant.
- Research on C60’s health effects is ongoing, with some promising but conflicting results.